

Check the code book which is provided (see links on the left hand side) to select the desired settings.Please note that this emulator is a Beta version. You you will be able to use this machine to both encrypt or decrypt Enigma messages (Enigma encryption is symmetric, which means that the same settings can be used to both encrypt or decrypt a message). To gain a better understanding of the encryption techniques used by the Enigma machine we have decided to recreate a virtual Enigma machine/emulator. Being able to decrypt German messages gave the Allies valuable information which has had a major impact on the outcomes of WWII. The first wartime Enigma messages were broken in January 1940. Together they developed a complex machine called the Bombe used to workout Enigma settings from intercepted German communications. He worked alongside Tony Kendrick, Peter Twinn, Alan Turing and Gordon Welchman. Dilly Knox, one of the former British World War I Codebreakers, set up an Enigma Research Section at Bletchley Park, England. In 1939, with the prospect of war, the Poles decided to share their findings with the British. A team of Polish cryptanalysts was the first to break Enigma codes as early as 1932, however the German used more advanced Enigma machines making it virtually impossible to break the Enigma code using traditional methods. One of the key objectives for the Allies during WWII was to find a way to break the code to be able to decrypt German communications.

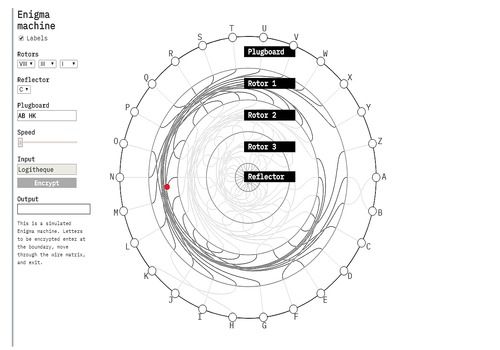
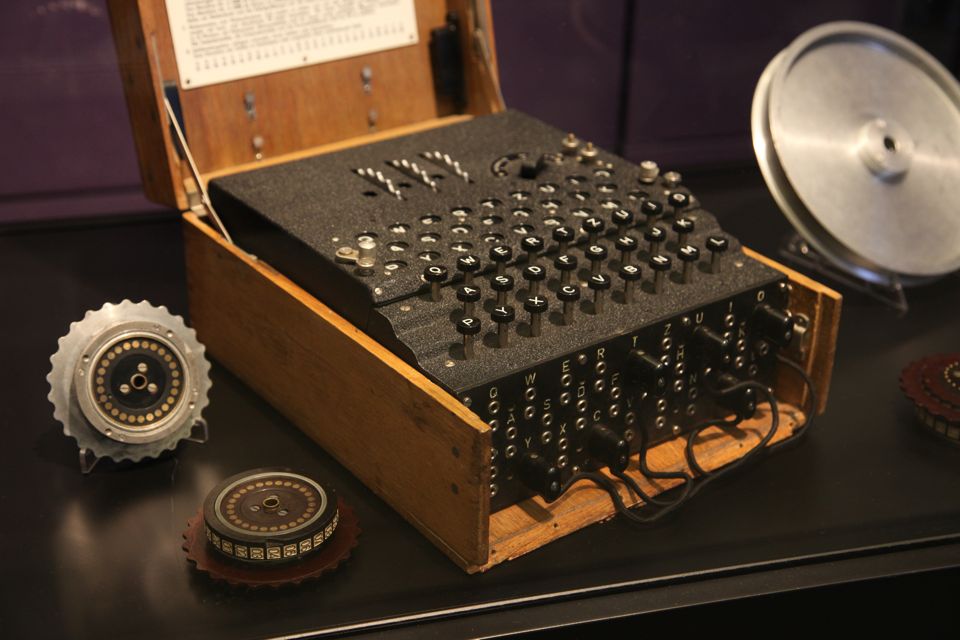
Enigma machines became more and more complex and were heavily used by the German army during World War II to encrypt radio signals. The first machines were invented at the end of World War I by German engineer Arthur Scherbius and were mainly used to protect commercial, diplomatic and military communication. The Enigma machines are a series of electro-mechanical rotor cipher machines.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
